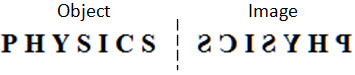|
|
Reflection of LightReflectionReflection of light is the change in direction of light rays that strike the boundary between different mediums.
Terms Used
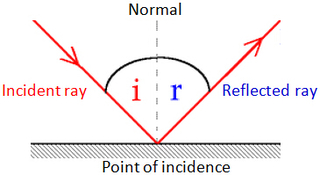
Two Laws of ReflectionFirst Law: The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the surface all lie in the same plane.
Second Law: The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. i.e i = r. Types of ReflectionAll surfaces reflect light but the smoothness of a surface affects the reflection of light.
5 Characteristics of Mirror ImageNote:
Virtual image is an image that cannot be captured on a screen; Real image is an image that can be captured on a screen. Virtual image is always upright whereas real image is inverted. “Laterally inverted” can be seen as “a reflection of object about the rightmost end”. Example: Tip: Image can be easily obtained by doing a reflection about the imaginary line.
An interesting video on a typical O-Level MCQ question: What happen to the size of the image when the object is moved nearer to the mirror? Check it out now! Constructing Ray Diagram for Plane Mirror
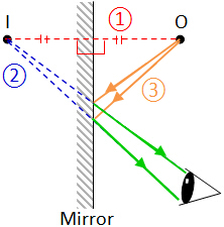
Note that we normally draw two light rays to locate position of mirror image. Likewise for extended objects, we can use same steps to locate the image.
Example:
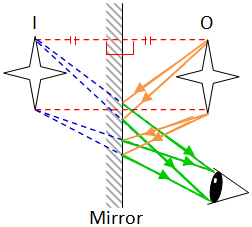
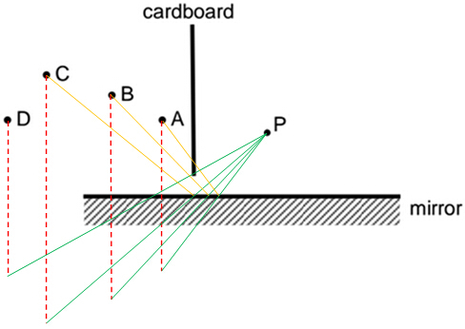
Four pins A, B, C and D are placed in front of a mirror. A student P is standing behind a cardboard. Which image(s) can be seen by the student? Answer:
Using the steps in constructing the ray diagram for mirror, only B and C can be seen by student P. |
|