|
|
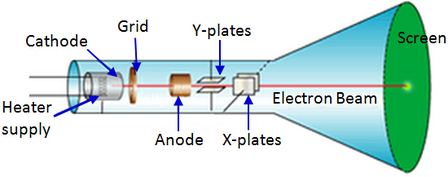
Cathode Ray OscilloscopeCathode Ray Oscilloscope (C.R.O)The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope is a common electronic device used to study waveforms, measure voltage and short intervals of time.
Structure of C.R.O
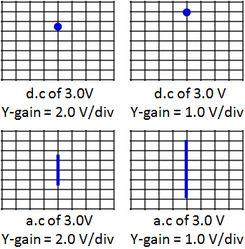
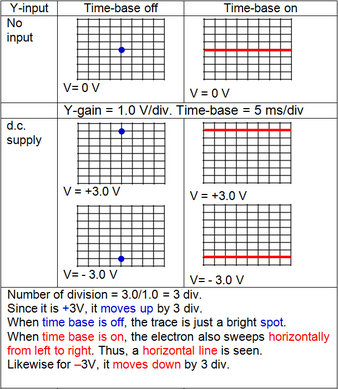
Y-gain & Time Base(1) Y-gain or Voltage gain
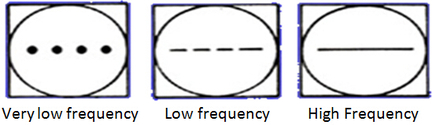
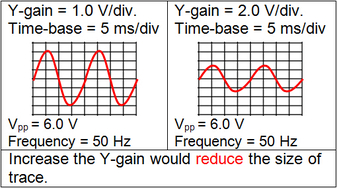
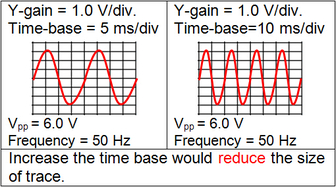
This amplifies the deflection of electron beam. The amount of deflection depends on the input voltage at Y-plates. Y-gain also determines the sensitivity of the oscilloscope. Unit: Volts per division, V/div A Y-gain of 1.0 V/div means that for an input of 2.5 V, the deflection would be 2.5 divisions (= 2.5 / 1.0 = 2.5). (2) Time base When time base is on, a voltage is applied to the X-plate. Time base controls the speed at which the electron beam sweep across the screen from left to right horizontally, then jump back to left plate and the sweeping repeats. This is done by altering the frequency of the time base. Effect of different time base setting Unit: millisecond/division (ms/div) or Hz
Conversion between ms/div and Hz Time base frequency is 25 Hz means the electron beam sweeps across the screen 25 times in one second. Note that each screen of C.R.O has a fixed number of divisions, i.e. 8. This means each time the electron beam sweeps across the screen, it moves 8 divisions. Therefore, in one second, it sweeps across 25 * 8 = 200 divisions. So time base = 1 / 200 = 0.005 s/div = 5 ms/div. Note that Y-gain and Time base are similar to the scale of a graph. Y-gain is for y-axis while Time base is for x-axis. Application of C.R.O
(2) Displaying Voltage Waveform
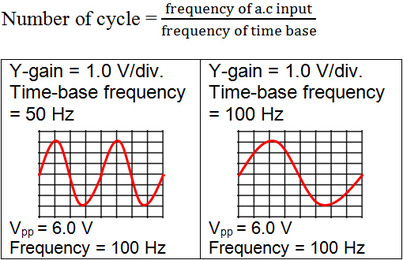
When time base is on with a suitable frequency, a steady waveform of any input voltage can be displayed on the screen. The period of each wave and number of complete wave displayed can be varied, and it is determined by the formula: (3) Measuring Short Intervals of Time
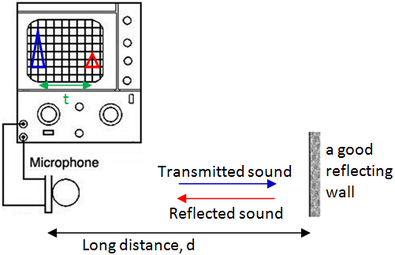
When time base is on, C.R.O can be used to measure a short interval of time. One of the examples is to measure the time taken for sound to travel a distance and hence find the speed of sound.
Note that the height of second pulse is smaller than that of first pulse because some energy is lost to the medium and the reflecting wall.
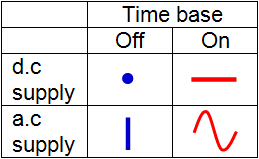
Screen Displays
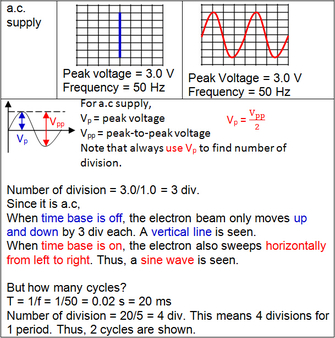
When time base is on and input is an a.c supply.
In summary,
Example
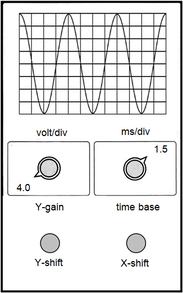
(a) Explain how the electron beam can be deflected to any spot on the fluorescent screen. (b) A waveform is displayed on the C.R.O screen as shown.
Answer:
(a) Potential differences are applied to X and Y plates respectively to deflect the electron beam horizontally or vertically. (b)(i) Vp = 4.0 * 4 = 16 V (ii) T = 1.5 * 10^(-3) * 4 = 6.0 * 10^(-3) s f = 1 / T = 167 Hz (iii) Changes observed:
|
|