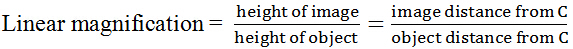|
|
LensLenses are used to converge or diverge a light beam.
Two types of Lens
Note
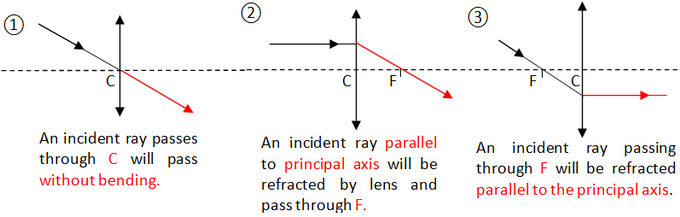
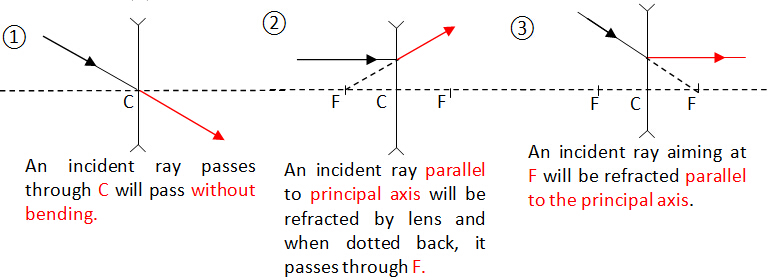
Ray Diagrams for Converging LensThree special rays for converging lens
Any two of these three light rays will help us to locate the position of image.
How?
Note that all the light rays from object must intersect at one point which is the position of image. Of course, the light rays from the tip of object go to the tip of image while the tail of object goes to the tail of image.
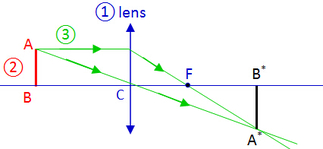
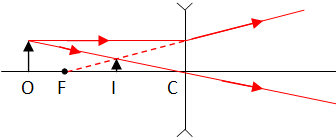
Example: Ray 2 and 3 are special light rays used to locate the position of image. Once image is located, the rest of light rays (1, 4, 5) join themselves to the point of intersection to complete the ray diagrams. Types of Images Formed
An animation on these ray diagrams can be found here. Or you can move around the object yourselves using the applet found above. Both give you the same result.
Note:
To determine the size of image, we can treat u = 2f (image is same size) as a reference.
Linear magnification is the ratio of image height to the object height. i.e
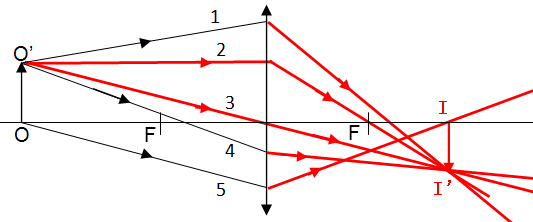
Ray diagram for Diverging Lens (Optional)Three special rays for diverging lens
Any two of these three light rays will help us to locate the position of image.
How? Image formed by diverging lens is always virtual, upright and diminished.
Note that when the object is closer to the lens, the size of image is larger. An animation on ray diagrams for different object distance can be found here. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||