|
|
FuseA fuse is safety device to prevent excessive current flow and hence protect wires and electrical appliance from overheating and damaged. It has the same function as circuit breaker. However, unlike a circuit breaker that can be reset after it trips, a fuse must be replaced after it blows.
Points to take note:
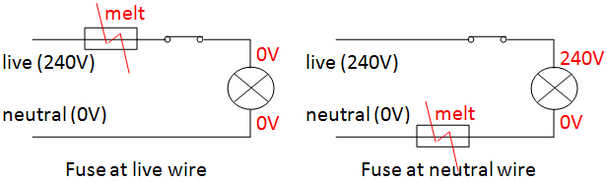
(1) Fuse Rating All fuses have a rated value. The value (fuse rating) indicates the maximum current that can flow through a fuse before it blows. The fuse should be chosen at a rating slightly higher than the current the electrical appliance draws under normal working conditions. If a fuse with a much higher rating is chosen, it will allow a current much greater than the current drawn by the appliance to pass. This large current will cause the appliance to overheat and be damaged before the fuse blows. If a fuse with a lower rating is chosen, the fuse will melt very quickly and break the circuit. The appliance might not work. Common fuse rating: 1A, 2A, 3A, 5A, 10A, 13A, 15A and 30A (2) A fuse must be connected to live wire. Reason: When the current flowing exceeds its current rating, the fuse will melt and disconnect the high potential of 240 V from the appliance if the fuse is connected to live wire. If fuse is connected to the neutral wire, the high potential of the live wire is not being cut off and the user might get electric shock when touched although the fuse is melt. |
|